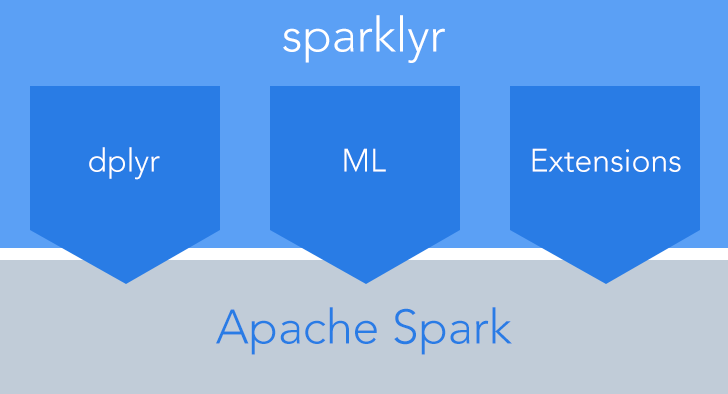
sparklyr-R语言访问Spark的另外一种方法
Spark自带了R语言的支持-SparkR,前面我也介绍了最简便的SparkR安装方法,这里我们换个方式,使用Rstudio提供的接口,sparklyr。
- 提供了完整的 dplyr后台实现
- 方便与Spark MLlib or H2O Sparkling Water整合
- 方便基于SPARK API编写自己的扩展
安装(记得安装Java虚拟机),
devtools::install_github("rstudio/sparklyr")
#install.packages("sparklyr")
#以上两种方法都可以
library(sparklyr)
#选择spark和hadoop的版本
spark_install(version = "2.0.1",hadoop_version = "2.7")
连接Spark
library(sparklyr) sc <- spark_connect(master = "local")
读取数据
#install.packages(c("nycflights13", "Lahman"))
library(dplyr)
iris_tbl <- copy_to(sc, iris)
flights_tbl <- copy_to(sc, nycflights13::flights, "flights")
batting_tbl <- copy_to(sc, Lahman::Batting, "batting")
列出所有的表
>src_tbls(sc) [1] "batting" "flights" "iris"
使用dplyr
# filter by departure delay and print the first few records >flights_tbl %>% filter(dep_delay == 2) ## Source: query [?? x 19] ## Database: spark connection master=local[8] app=sparklyr local=TRUE ## ## year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time ## <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int> ## 1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830 ## 2 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923 ## 3 2013 1 1 702 700 2 1058 ## 4 2013 1 1 715 713 2 911 ## 5 2013 1 1 752 750 2 1025 ## 6 2013 1 1 917 915 2 1206 ## 7 2013 1 1 932 930 2 1219 ## 8 2013 1 1 1028 1026 2 1350 ## 9 2013 1 1 1042 1040 2 1325 ## 10 2013 1 1 1231 1229 2 1523 ## # ... with more rows, and 12 more variables: sched_arr_time <int>, ## # arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>, tailnum <chr>, ## # origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, ## # minute <dbl>, time_hour <dbl>
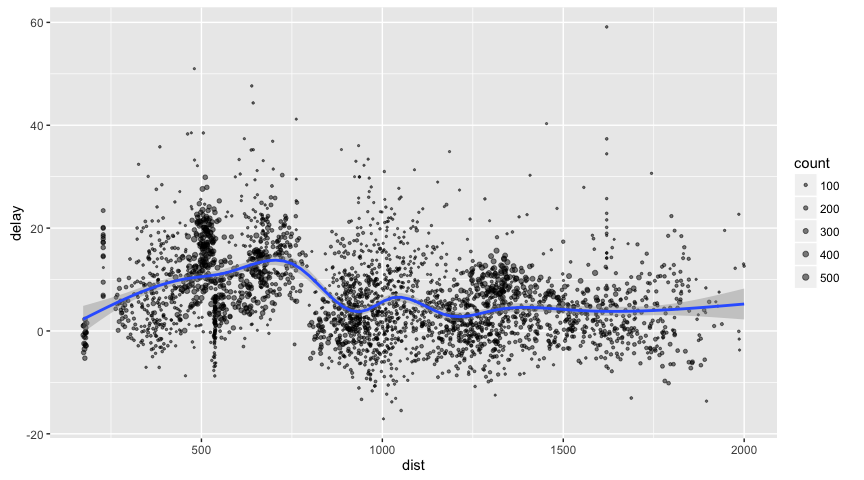
画图
delay <- flights_tbl %>% group_by(tailnum) %>% summarise(count = n(), dist = mean(distance), delay = mean(arr_delay)) %>% filter(count > 20, dist < 2000, !is.na(delay)) %>% collect # plot delays library(ggplot2) ggplot(delay, aes(dist, delay)) + geom_point(aes(size = count), alpha = 1/2) + geom_smooth() + scale_size_area(max_size = 2)
开窗函数Window Function
batting_tbl %>% select(playerID, yearID, teamID, G, AB:H) %>% arrange(playerID, yearID, teamID) %>% group_by(playerID) %>% filter(min_rank(desc(H)) <= 2 & H > 0) ## Source: query [?? x 7] ## Database: spark connection master=local[8] app=sparklyr local=TRUE ## Groups: playerID ## ## playerID yearID teamID G AB R H ## <chr> <int> <chr> <int> <int> <int> <int> ## 1 abbotpa01 2000 SEA 35 5 1 2 ## 2 abbotpa01 2004 PHI 10 11 1 2 ## 3 abnersh01 1992 CHA 97 208 21 58 ## 4 abnersh01 1990 SDN 91 184 17 45 ## 5 abreujo02 2015 CHA 154 613 88 178 ## 6 abreujo02 2014 CHA 145 556 80 176 ## 7 acevejo01 2001 CIN 18 34 1 4 ## 8 acevejo01 2004 CIN 39 43 0 2 ## 9 adamsbe01 1919 PHI 78 232 14 54 ## 10 adamsbe01 1918 PHI 84 227 10 40 ## # ... with more rows
使用SQL
library(DBI) iris_preview <- dbGetQuery(sc, "SELECT * FROM iris LIMIT 10") iris_preview ## Sepal_Length Sepal_Width Petal_Length Petal_Width Species ## 1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa ## 2 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa ## 3 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa ## 4 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa ## 5 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa ## 6 5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4 setosa ## 7 4.6 3.4 1.4 0.3 setosa ## 8 5.0 3.4 1.5 0.2 setosa ## 9 4.4 2.9 1.4 0.2 setosa ## 10 4.9 3.1 1.5 0.1 setosa
机器学习
# copy mtcars into spark
mtcars_tbl <- copy_to(sc, mtcars)
# transform our data set, and then partition into 'training', 'test'
partitions <- mtcars_tbl %>%
filter(hp >= 100) %>%
mutate(cyl8 = cyl == 8) %>%
sdf_partition(training = 0.5, test = 0.5, seed = 1099)
# fit a linear model to the training dataset
fit <- partitions$training %>%
ml_linear_regression(response = "mpg", features = c("wt", "cyl"))
## * No rows dropped by 'na.omit' call
fit
## Call: ml_linear_regression(., response = "mpg", features = c("wt", "cyl"))
##
## Coefficients:
## (Intercept) wt cyl
## 37.066699 -2.309504 -1.639546
summary(fit)
## Call: ml_linear_regression(., response = "mpg", features = c("wt", "cyl"))
##
## Deviance Residuals::
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.6881 -1.0507 -0.4420 0.4757 3.3858
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 37.06670 2.76494 13.4059 2.981e-07 ***
## wt -2.30950 0.84748 -2.7252 0.02341 *
## cyl -1.63955 0.58635 -2.7962 0.02084 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## R-Squared: 0.8665
## Root Mean Squared Error: 1.799
读写数据
temp_csv <- tempfile(fileext = ".csv") temp_parquet <- tempfile(fileext = ".parquet") temp_json <- tempfile(fileext = ".json") spark_write_csv(iris_tbl, temp_csv) iris_csv_tbl <- spark_read_csv(sc, "iris_csv", temp_csv) spark_write_parquet(iris_tbl, temp_parquet) iris_parquet_tbl <- spark_read_parquet(sc, "iris_parquet", temp_parquet) spark_write_csv(iris_tbl, temp_json) iris_json_tbl <- spark_read_csv(sc, "iris_json", temp_json) src_tbls(sc) ## [1] "batting" "flights" "iris" "iris_csv" ## [5] "iris_json" "iris_parquet" "mtcars"
编写扩展
# write a CSV
tempfile <- tempfile(fileext = ".csv")
write.csv(nycflights13::flights, tempfile, row.names = FALSE, na = "")
# define an R interface to Spark line counting
count_lines <- function(sc, path) {
spark_context(sc) %>%
invoke("textFile", path, 1L) %>%
invoke("count")
}
# call spark to count the lines of the CSV
count_lines(sc, tempfile)
## [1] 336777
dplyr Utilities
tbl_cache(sc, "batting") #把表载入内存 tbl_uncache(sc, "batting") #把表从内存中卸载
连接Utilities
spark_web(sc) #Spark web console spark_log(sc, n = 10) #输出日志
关闭与Spark的连接
spark_disconnect(sc)